Violence against children occurs in every region and country, and in almost every context. The root causes do not lie in any one culture, tradition or institution, but in the wider structural issues, social norms and deep-rooted beliefs and behaviours that shape gender and authority:
- Gender discriminatory norms that shape the dominance of men and the subservience of women and the right to preserve that dominance through violence are found in some form in almost every culture. The pressure to conform to dominant gender norms is high. Young people who do not choose to or cannot conform – such as LGBTI people, or those who have not learned the ‘proper’ behaviour – can be sanctioned through violence.
- Social norms that shape authority, traditionally male and adult, usually include the legitimacy to teach, discipline and control, and to use violence to maintain that authority. These norms support the authority of male and female teachers over children, often using some form of violence to maintain that authority and reinforce social and gender norms.
- Wider structural and contextual factors including conflict, income inequality, deprivation or marginalization and weak systems. In addition, the borderless nature of social media enables violence – such as cyber-bullying, online grooming and trolling – in spaces that that are hard to police and regulate with existing state-bound tools.
Schools and the wider education system operate within social and structural frameworks. Within the educational system, these dynamics produce and reproduce environments that do not protect children. In fact, the system potentially exposes them to forms of violence that replicate, reinforce and recreate the norms and power dynamics of the societies, communities and families around them. Policy-makers, authority figures, teachers, parents, other students and community members participate in and create these dynamics. Changing them therefore requires coordinated work at all levels and across all sectors.
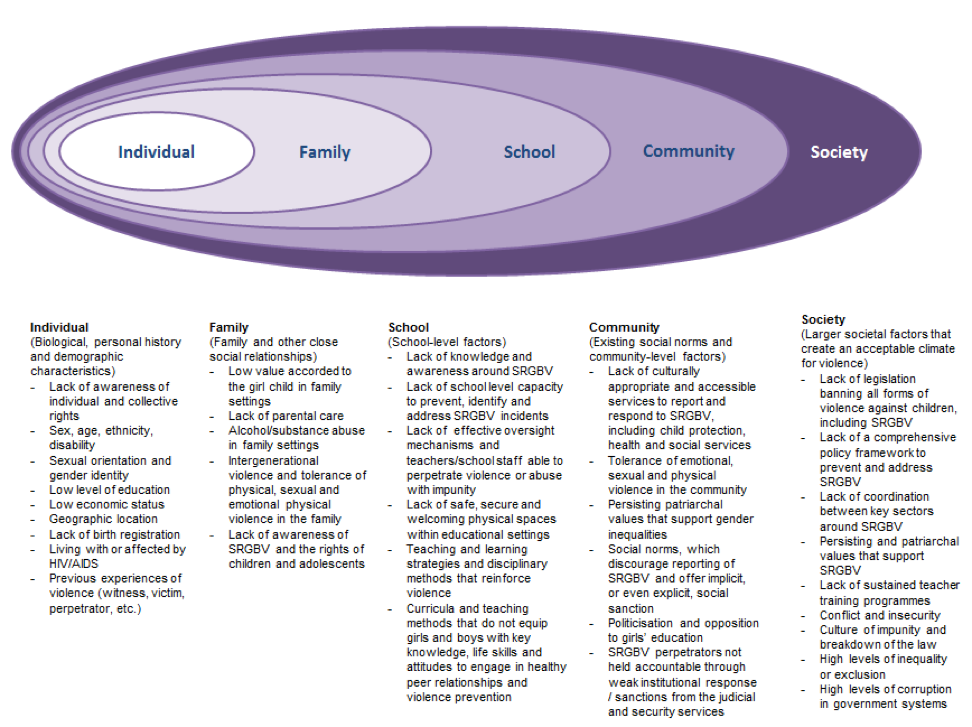
What are the risk factors?
A variety of risk factors intersect at the individual, family, school, community and societal (including the institutional/state) level to increase the risk of SRGBV. These factors, represented in the ecological model below , will vary according to the context and situation, requiring a thorough analysis at the local level prior to designing interventions (see Section 2.6 for Situation analysis/needs assessment (formative research)).
Risk factors for SRGBV